Chelating agents play an important role in the production of water-soluble liquid fertilizers. Its main function is to combine with metal ions to form stable properties and thus improve solubility., Bioavailability and stability of water-soluble fertilizers. In agriculture, chelating agents in the production of chelates in the production of liquid fertilizers often used to prevent the precipitation of trace elements and improve the absorption capacity of crops. During the production of water-soluble fertilizers, Chelating agents are added to the reactor equipment. SX.Make water soluble fertilizer nutrition sufficient.
What chelates in the production of water-soluble liquid fertilizers ca
The following are chelating agents commonly used in the production of water-soluble liquid fertilizers:
Acid etilendiaminotetraacético (EDTA). EDTA is one of the most used chelating agents in the production of water-soluble fertilizers.. Can effectively chelate a variety of metal ions, including iron, copper, manganese, zinc, etc. Application of EDTA in water-soluble fertilizers helps to improve the solubility of trace elements and the absorption efficiency of plants.
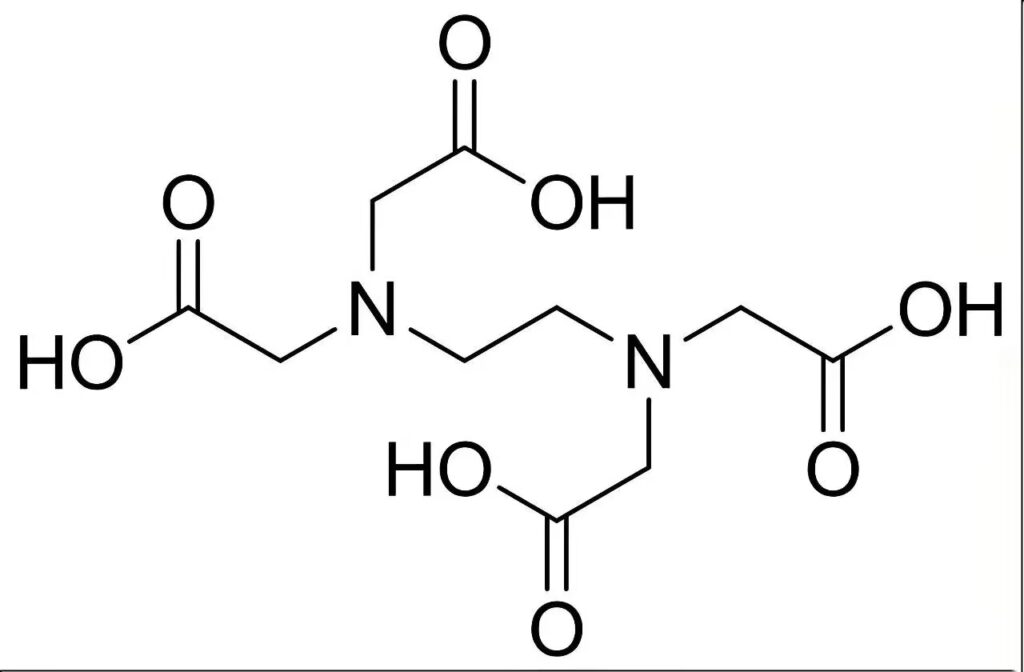

Acid dietilentriaminopentaacético (DTPA). DTPA is a more powerful chelating agent than EDTA, especially in alkaline environments. It is mainly used to chelate iron ions to prevent iron from precipitating into insoluble compounds under alkaline conditions.. DTPA ensures that plants can absorb iron effectively in high pH soils.

Hydroxyethylidene diphosphonic acid (HEDP). HEDP is commonly used to prevent the precipitation of alkaline earth metal ions such as calcium and magnesium.. In hard water conditions, can effectively maintain the dissolved state in water, prevent the formation of precipitation of these elements and guarantee the stability and effectiveness of the fertilizers.

How to choose different chelating agents when producing water-soluble liquid fertilizers?
The choice of chelating agent depends on a variety of factors such as soil pH, Water-soluble fertilizer formulation and cost considerations. The following are key factors to consider when choosing a chelating agent:
Environmental pH. The stability and effectiveness of chelating agents will differ under acidic and alkaline conditions.. DTPA is suitable for use in alkaline soils, while EDTA works best in neutral or slightly acidic conditions.
Rentable. Some chelating agents are more expensive and, por tanto, can be used less frequently in the production of low-cost fertilizers. For example, nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) It is relatively cheap and, therefore, It is widely used in some low-cost water-soluble fertilizer formulations.
Plant Types and Requirements. Different crops have different trace element needs, so chelating agents should be selected according to the specific needs of crops when formulating fertilizers.












